Tel: 0755-23359557
15013713572(微信同号)
Fax: 0755-23504001
E-mail: hp_zheng@xgzxwdz.com
Zip Code: 518034
Introduction of MCU Mainstream Chip Company and Its Product Characteristics
The Chinese name of MCU(MicroControllerUnit) is Microcontrol Unit, also known as SingleChipMicrocomputer. It means that with the emergence and development of large-scale integrated circuits, the CPU, RAM, ROM, timer and a variety of I/O interfaces of the computer are integrated on a chip to form a chip-level computer, which performs different combination control for different applications. In fact, to put it simply, it is what we usually call a single chip microcomputer.
Singlechip was born in 1971 and has gone through three stages: SCM, MCU and SoC. Singlechip has developed from 1-bit, 4-bit, 8-bit and 16-bit to 32-bit and even 64-bit. With the rapid development of consumer electronics products since the 1990s, the single chip technology has been greatly improved. A number of single chip manufacturers that have passed the market test and gained good reputation have been born one after another. Let's look at the original MCU chip factory and its product introduction.
Foreign manufacturers:
In the past ten years or so, the rapid rise of the mobile market, the birth of the Arm Cortex-M series, and the help of manufacturers such as ST, NXP, TI and Resa, MCU has shifted from the early contention of a hundred schools to the market dominated by ARM Cortex-M. Take the domestic market as an example. According to IHS data, MCU with Arm core occupies about 15% of the domestic market. With the help of Arm core and ecology, domestic MCU manufacturers have mushroomed and achieved several local giants. However, we find that the gap is still obvious.
Relevant data show that leading MCU manufacturers including ST, NXP and Infineon (including the acquired Cypress) in Europe, TI, Microchip and Resa in Japan in the United States almost dominate the high-end market including automotive electronics and motor control. These manufacturers also occupy more than 80% of the MCU market, and with the rise of new applications, this number is bound to continue to rise.
In the second decade of the 21st century, MCU market seems to be experiencing some new changes.
Status Quo: Foreign Countries Lead Far
In the earlier article "Ten Years of MCU Jianghu" observed by the semiconductor industry, the author talked about Arm MCU gradually becoming the mainstream and the rise of several MCU manufacturers in the past ten years. The article also explains the reasons why Arm and foreign manufacturers such as ST can dominate the Jianghu. However, as mentioned above, domestic MCU has little influence in this seemingly standardized environment. Apart from the relatively slow entry, it is also closely related to the current competitive situation of local MCU manufacturers.
According to incomplete statistics, the number of MCU manufacturers in China has exceeded 100, and many of them are aiming to replace foreign manufacturers to make a "quick buck". The operation mode of these enterprises is also quite simple. Depending on which foreign manufacturer's MCU is selling well in China, or grasping the products that foreign manufacturers are about to withdraw from the market, they will follow the lead of a pin compatible product and replace it with a lower price. This has resulted in crowded racetracks and low profits. The chip industry, which originally focused on design, has been transformed into an industry that wins with supply and manufacturing costs. This has limited the growth of the company and is not conducive to the development of the entire industry.
According to senior experts in the industry, semiconductor industry observers told reporters that European, American and Japanese manufacturers were able to win over most MCU markets mainly because they set a benchmark for their customers in the four aspects of products, software and the ecological environment in which they were used, while setting up barriers that other competitors could not easily surmount.
First look at the product; Leading foreign manufacturers basically have their own IP, but most of their domestic peers have incomplete IP, and many of them bring the existing IP to piece together to develop products, which makes their products have inherent "defects" from the beginning of their birth. In addition, foreign MCU manufacturers have experienced long-term cultivation in different industries and even started to support the industries from scratch. Their understanding of many industry specifications has been reflected in the internal and external design of MCU, which is also lacking in local MCU.
Second, look at the software. The so-called software algorithm is based on the needs of the industry and customers, from simple hardware accumulation to understanding the needs of customers and then creating with customers. In this process, it is inseparable from MCU company's focus on software and algorithms. In the past, many algorithms used to require software processing. However, because foreign enterprises had a thorough understanding of specific industries and took a long time to process, they had a thorough understanding of the customer's usage scenarios, systems, software algorithms, etc., and then jointly created and implemented them with chips, including other devices around the main chip as much as possible inside the chip. This not only saves the cost, but also makes the product easier to develop.
Third, look at ecology. The ecology of MCU includes two aspects: first, whether the whole design, production, processing and manufacturing of MCU are complete. For example, during processing, the customer will be very familiar with a certain mass production programming device during the production process. If a mass production burning tool is to be replaced, the customer's production line will need to be re-purchased, re-trained, etc., which will affect the production. Therefore MCU manufacturers must take this ecology into account. The second aspect that ecology needs to consider is whether there is perfect information, abundant online resources, good reputation and flow support in the customer design process.
These leading manufacturers have seized the MCU market by virtue of one step and profound technological advantages. This makes it very difficult for domestic MCU manufacturers to compete with them in the general MCU market.
Opportunity: New Changes in Industry
While Arm and its partners continue to expand and strengthen the general MCU market hand in hand, some new "variables" have emerged in the global MCU market. For example, the popularity of RISC-V and the emergence of the Internet of Things have pushed MCU SoC to become a new trend, which will become the "icebreaker" of the current MCU pattern.
First look at RISC-V As we all know, this is an open source instruction set. According to David Patterson in his book RISC-vReader: An Open Architecture Atlas, unlike almost all ISA in the past, RISC-V is unusual in that it is modular. Its core ISA basic ISA called RV32I, which runs a complete software stack. RV32I is fixed and will never change. This provides a stable target for compiler writers, operating system developers and assembly language programmers. Modularity comes from optional standard extensions, which may or may not be included in the hardware depending on the needs of the application. This modularity makes RISC-V compact and low energy consumption, which may be crucial for embedded applications.
It is precisely because of this open source feature that RISC-V attracts both established MCU manufacturers and emerging suppliers to enter this track. Just because this is a new field, MCU manufacturers at home and abroad have little difference in technology and ecology. This is also one of the factors that the author regards it as a new change in MCU market.
Look again, the rise of the Internet of Things also makes MCU face unprecedented new changes.
As a vertically subdivided market, the Internet of Things has more demands on MCU and its peripheral components. Besides AI, sensors (analog front-end) and wireless (communication) etc. are also gradually becoming standard in MCU application design. More importantly, different Internet of Things applications have different requirements on the power consumption and functions of MCU and related components, which has given rise to a wider range of MCU SoC requirements. Developing MCU with different functions for different fields has become the industry norm.
In addition, while Arm MCU is popular, there are many MCU with other cores that have good market performance in the market. This was also mentioned in the author's previous article "Ten Years of MCU Jianghu". From another perspective, there is still room for self-developed core (non-Arm/ non-RISC-V)MCU enterprises in areas not covered by these cores. If we can seize the first-mover advantage, this will also be another breakthrough point for domestic MCU.
Future: Challenges
Although the opportunity of domestic MCU is before us, the development of many technologies shows that this will not be achieved overnight.
First look at RISC-V NXP senior MCU expert Liang ping once wrote in his book "how can we make RISC-V a big cake?" "The article mentioned that the ecosystem of an MCU product determines whether the development resources and support that developers of this product can access are comprehensive and diversified, convenient to use, easy to learn and understand, stable and reliable, etc. Take a general MCU as an example, usually these resources and support roughly include the contents in the following figure.
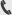 Support hotline:
Support hotline:
